High-Speed Counters (HSC) in PLC: Working, Encoder Integration, Configuration, Applications & Optimization
A high-speed counter is a vital component in modern PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems, designed to accurately count input pulses / events at extremely fast rates. These counters are widely used in industrial automation and motion control applications where precision is critical, such as CNC machines, conveyor systems, and robotic arms. By processing rapid digital input frequency signals that regular PLC inputs might miss, high-speed counters ensure accurate pulse counting, direction detection, and position feedback. Integrating them with encoders allows for real-time monitoring of speed, rotation, and movement, making them indispensable for high-performance manufacturing and automated systems.
What is a High-Speed Counter (HSC) in PLC?
What is a high-speed counter? A High-Speed Counter (HSC) is a specialized feature in a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) or control system designed to count input pulses / events at a very high rate. Unlike normal PLC inputs, which may miss fast signals due to scan cycle limitations, HSC modules can track thousands of pulses per second, making them essential for industrial automation and motion control applications.
In industries across the USA, HSCs are widely used in manufacturing to count products on assembly lines, monitor machine rotations, and capture precise position feedback. They help measure speed and direction accurately, especially when paired with encoders. The technology is reliable for applications where event counting must be precise and fast, such as robotic arms or conveyor systems.
How Does a High-Speed Counters in PLC Work?
How does a high-speed counter work? The HSC works by counting every digital input pulse it receives. These pulses can represent movement, rotations, or other events. Using rising edge / falling edge detection, the counter can increment or decrement values. Depending on the type of counter, it can operate as a single-phase counter for simple counting or a two-phase counter for direction detection.
Some HSC modules also support quadrature encoder signals, which provide both direction detection and position. These counters process pulses in real-time, bypassing normal PLC scan cycles. The HSC maintains accuracy even at high digital input frequencies, allowing operators to track rotational movement or speed measurement in complex machinery like CNC machines and automated production lines.
What is an Encoder and How Does it Generate Signals?
Differences between incremental and absolute encoders lie in how they provide position feedback. An encoder is a sensing device that measures motion, position, or speed and converts it into a feedback signal. Linear encoders track movement along a path, while rotary encoders / hollow shaft encoders / thru-bore encoders track rotational motion.
Absolute encoders provide unique signals for each position, so they know exact locations even after power loss. Incremental encoders count pulses from a starting reference and require a home position after restart. Encoders produce square wave pulses or digital signals, which the HSC module interprets to calculate speed, direction, and position in real-time.
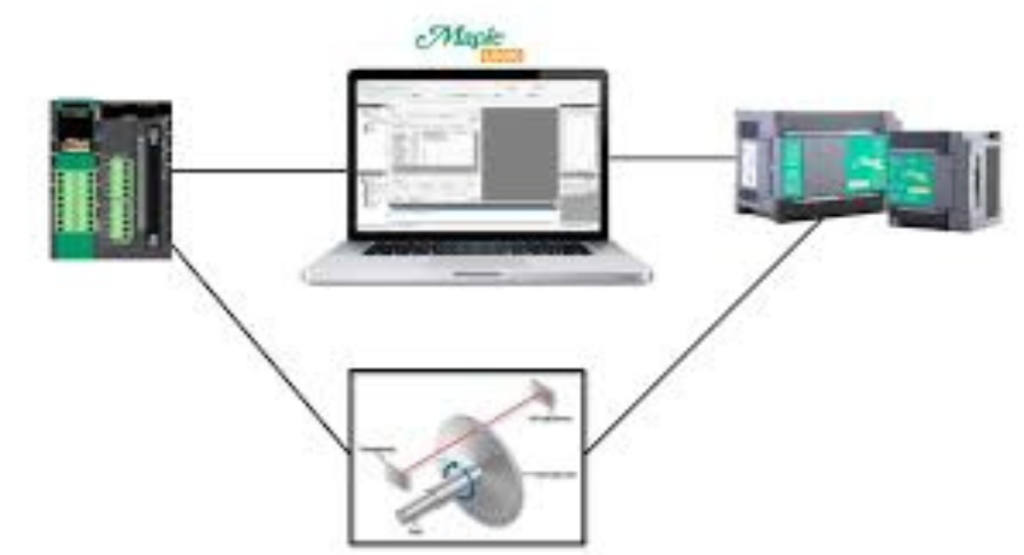
Using an Encoder with a High-Speed Counter
Using a high-speed counter with an encoder allows precise measurement of fast motion. The encoder output signal processing sends pulses to the HSC. Each pulse represents a small movement or rotation, and the HSC counts these events quickly. This enables accurate speed measurement, direction detection, and position tracking in automated systems.
The setup is common in motion control for robots and CNC machines. A quadrature encoder provides two signals, A and B channels, allowing the HSC to detect both movement and direction. With pulse counting integrated into the PLC, operators can maintain precise control over rotational movement, position, and speed.
How PLC Interprets Encoder Signals Through HSC
How does a PLC interpret encoder signals? The PLC reads encoder pulses through the HSC module. In single-phase vs two-phase high-speed counters, a single-phase HSC counts only rising edges, which is suitable for simple movement detection. A two-phase HSC counts both rising and falling edges from two channels, providing accurate direction detection.

In quadrature mode counting in PLC, the HSC monitors Channel A and B signals, interpreting the sequence to determine clockwise or counterclockwise rotation. This method is vital for closed-loop control in machines, allowing operators to track position and adjust motion in real-time without missing high-speed events.
Applications of High-Speed Counters in Industrial Automation
High-speed counter applications in manufacturing include assembly line monitoring, pulse counting for packaging, and motion control in robotics. CNC machines use HSCs to track spindle rotations, ensuring accurate cuts and machining processes.
Other applications involve position feedback in conveyor systems, monitoring speed in motors, or measuring flow in automated pipelines. In these cases, HSC modules provide reliable event counting and help maintain precision in high-speed operations. A typical table of applications is shown below:
Application Area Use of HSC Encoder Type
Assembly Lines Count products Incremental
Robotics Motion control Quadrature
CNC Machines Track spindle Rotary
Conveyor Systems Position feedback Linear
H2: Configuring a High-Speed Counter in PLC Systems
Configuring high-speed counters in MapleLogic involves setting the counter type and input mode. Users choose between linear counters for single-direction counting and ring counters for rotational sequences. Input signals can be one-phase or two-phase depending on encoder type.
The HSC module can be set to compare mode, triggering actions when a count reaches a specific value. Operators also define unit time for RPM measurement or PPS measurement. Correct configuration ensures encoder signal processing is accurate, and all pulse counting is captured by the PLC.
Selecting the Right High-Speed Counter Module for Your Application
Choosing the correct HSC module depends on digital input frequency, encoder type, and environmental conditions. High-speed machinery may require modules supporting two-phase counters or quadrature encoder signals.
Small machines may only need a single-phase counter with basic position feedback, while industrial automation systems benefit from ring counters and advanced compare mode functions. Evaluating these requirements ensures optimal feedback for motion control systems.
Optimizing HSC Performance for Accuracy & Speed
Optimizing HSC performance involves proper wiring, shielded cables, and correct grounding to reduce noise. Operators can adjust pulse multiplication factors, debounce filters, and timing settings to improve precision.
Regular monitoring of signal transitions ensures accurate rotational movement readings. Optimized systems provide reliable speed measurement, correct direction detection, and precise encoder output signal processing, which is crucial in CNC machines and industrial automation.
Troubleshooting Common High-Speed Counter Issues
Troubleshooting high-speed counters starts with checking wiring, encoder alignment, and HSC configuration. Issues may include missing pulses, reversed direction detection, or inaccurate RPM measurement.
Using diagnostic tools in the PLC software, like MapleLogic, helps identify errors. Adjusting settings for single-phase vs two-phase high-speed counters, verifying encoder signals, and calibrating HSC modules solves most common problems in industrial systems.
Integration of HSCs with Other PLC Hardware
HSCs integrate seamlessly with I/O modules, motion controllers, HMIs, and SCADA systems. The integration allows live monitoring of speed, position, and direction detection.
Using closed-loop control, the PLC can adjust operations in real-time based on encoder feedback signals. This improves precision, reduces downtime, and enhances overall industrial automation performance across manufacturing lines and robotic systems.
Future Trends and Advancements in High-Speed Counter Technology
Future HSC modules are moving toward AI-assisted diagnostics, real-time analytics, and higher frequency handling. These trends allow predictive maintenance and more precise pulse counting.
Integration with IoT platforms and cloud-based monitoring is expanding in the USA. Advanced HSCs will provide enhanced feedback for motion control systems, support rotary and linear encoders, and enable smarter, more responsive industrial control systems in next-generation automation.
FAQs
- What is a high-speed counter in PLC?
A high-speed counter in PLC is a module or feature that counts rapid input pulses/events accurately, used for motion control, speed measurement, and industrial automation tasks. - What is a high-speed counter in IC?
A high-speed counter in an IC is an integrated circuit designed to count digital pulses at very high frequencies, often used in timing, frequency measurement, or digital systems. - What is high-speed counter software?
High-speed counter software is a program within a PLC or control system used to configure, monitor, and manage HSC modules, including pulse counting and encoder signal processing. - What is high-speed counter wiring diagram?
A high-speed counter wiring diagram shows how to connect encoders, HSC inputs, and PLC modules, including power, signal lines, and pulse input connections. - What is a high-speed counter module?
A high-speed counter module is a PLC add-on that processes high-frequency pulses from sensors or encoders to provide accurate position, speed, and direction feedback.
Meta Description
“Learn about best high-speed counters(HSC) in PLCs, their working, encoder integration, configuration, applications, and optimization.”






